Lucía Sanchís (US) — Modelling of fast-ion transport in fusion plasmas with symmetry-breaking fields
Don't miss any Success Story following us on X and LinkedIn!
@RES_HPC RES - Red Española de Supercomputación @res-icts.bsky.social
Check this Success Story at our LinkedIn: Modelling of fast-ion transport in fusion plasmas with symmetry-breaking fields
💡A Success Story about advancing towards sustainable fusion energy💡
📋 "Modelling of fast-ion transport in fusion plasmas with symmetry-breaking fields" led by Lucía Sanchís from Universidad de Sevilla
Confining high-energetic, suprathermal ions in magnetically confined fusion devices is essential for the viability of fusion as a sustainable energy source. Localised losses of these particles can significantly reduce the overall device efficiency, putting components in direct contact with the plasma in risk.
The project aimed to characterise the energetic ion transport in several key fusion devices: JT-60SA (Japan), Wendelstein 7-X (Germany), MAST-U (United Kingdom), and the currently under construction SMART fusion reactor in Seville to optimise its operational parameters
🖥️ Thanks to RES supercomputer #MareNostrum5 from Barcelona Supercomputing Center, the team made large-scale simulations with ASCOT5, a Monte Carlo code specifically designed to model suprathermal ion behaviour under realistic conditions. They took into account detailed ion sources, magnetic field geometries, plasma parameters, and 3D wall structures for each fusion device:
🔹W7-X: The low-mirror magnetic configuration had the highest overall ion losses, but not affecting the device integrity as they were mostly directed to shielded components.
🔹MAST-U: The ion losses were mainly attributed to resonant transport driven by ion–magnetic field interactions, which are modulated by the configuration of the external perturbation.
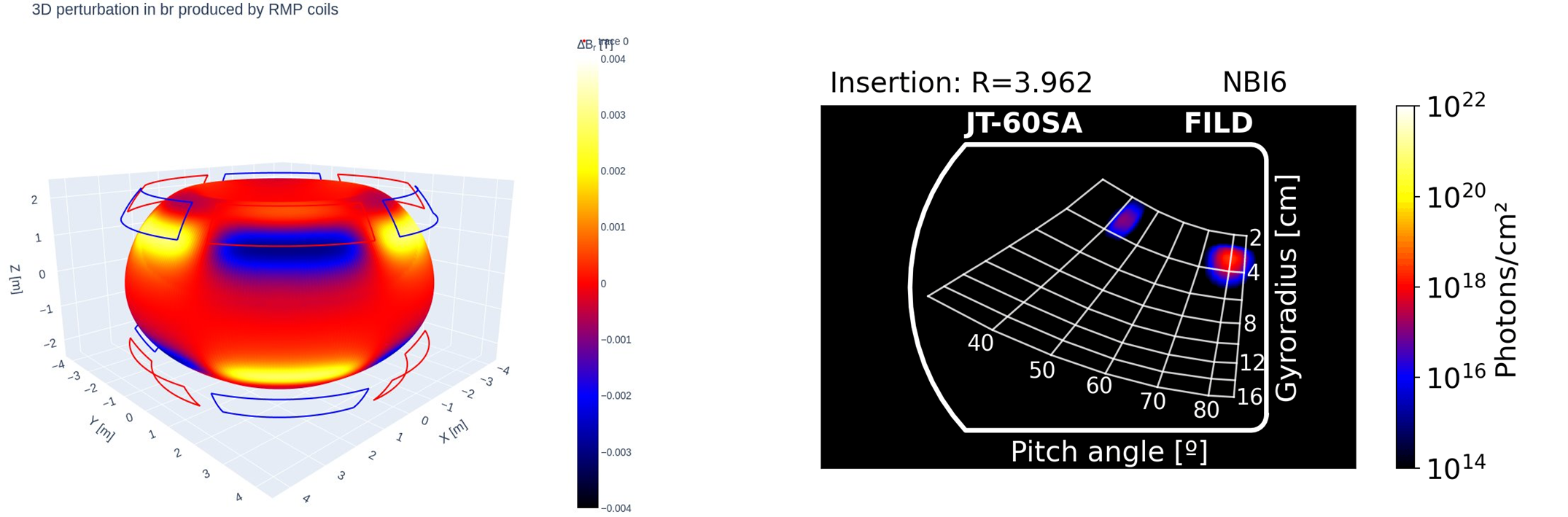
🔹JT60-SA: They focused on the evaluation of total energetic-ion losses to the reactor wall for assessing the mechanical integrity of the device. They generated synthetic signals for the Fast Ion Loss Detectors (FILD), enabling detailed characterisation of ion dynamics and supporting the optimisation of detector design and operation.
🔹SMART: They analysed slowing-down times and particle distribution under relevant plasma conditions.